Are you struggling to find the right answer to a tricky question? Look no further! We’ve got you covered with a simple guide to help you choose the best answer from the options provided.
Whether you’re taking a quiz, solving a problem, or just making a decision, knowing how to pick the right answer is key. Let’s dive in and uncover some tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
please select the best answer from the choices provided
Please Select the Best Answer from the Choices Provided
First and foremost, read through all the options carefully. Make sure you understand what each choice entails before making your selection. Take your time to analyze the information and eliminate any obviously incorrect answers.
Next, consider any hints or clues provided in the question itself. Sometimes, the wording or context can point you in the right direction. Use these clues to guide your decision-making process and narrow down your choices.
If you’re still unsure after the first two steps, try to eliminate any answers that are similar or redundant. Often, multiple options may seem correct at first glance, but upon closer inspection, you can rule out some choices based on their similarities.
Finally, trust your instincts. Sometimes, your initial gut feeling can lead you to the correct answer. Don’t second-guess yourself too much and go with the option that feels right to you. Remember, it’s okay to take a chance and make an educated guess if needed.
By following these simple guidelines, you’ll be able to select the best answer from the choices provided with confidence and ease. So, next time you’re faced with a tough decision, trust your judgment and make the choice that feels right for you.
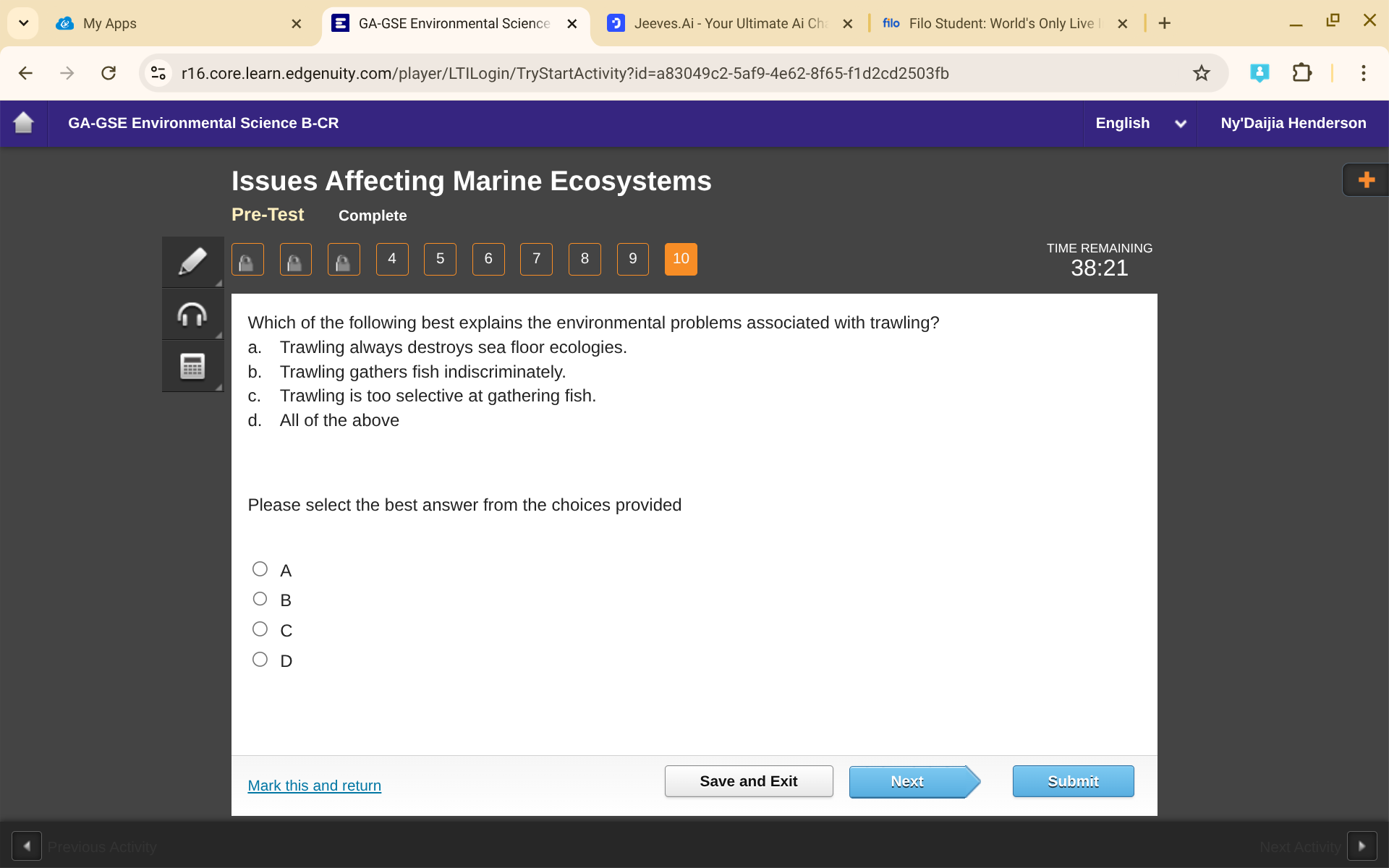
Which Of The Following Best Explains The Environmental Problems Associate
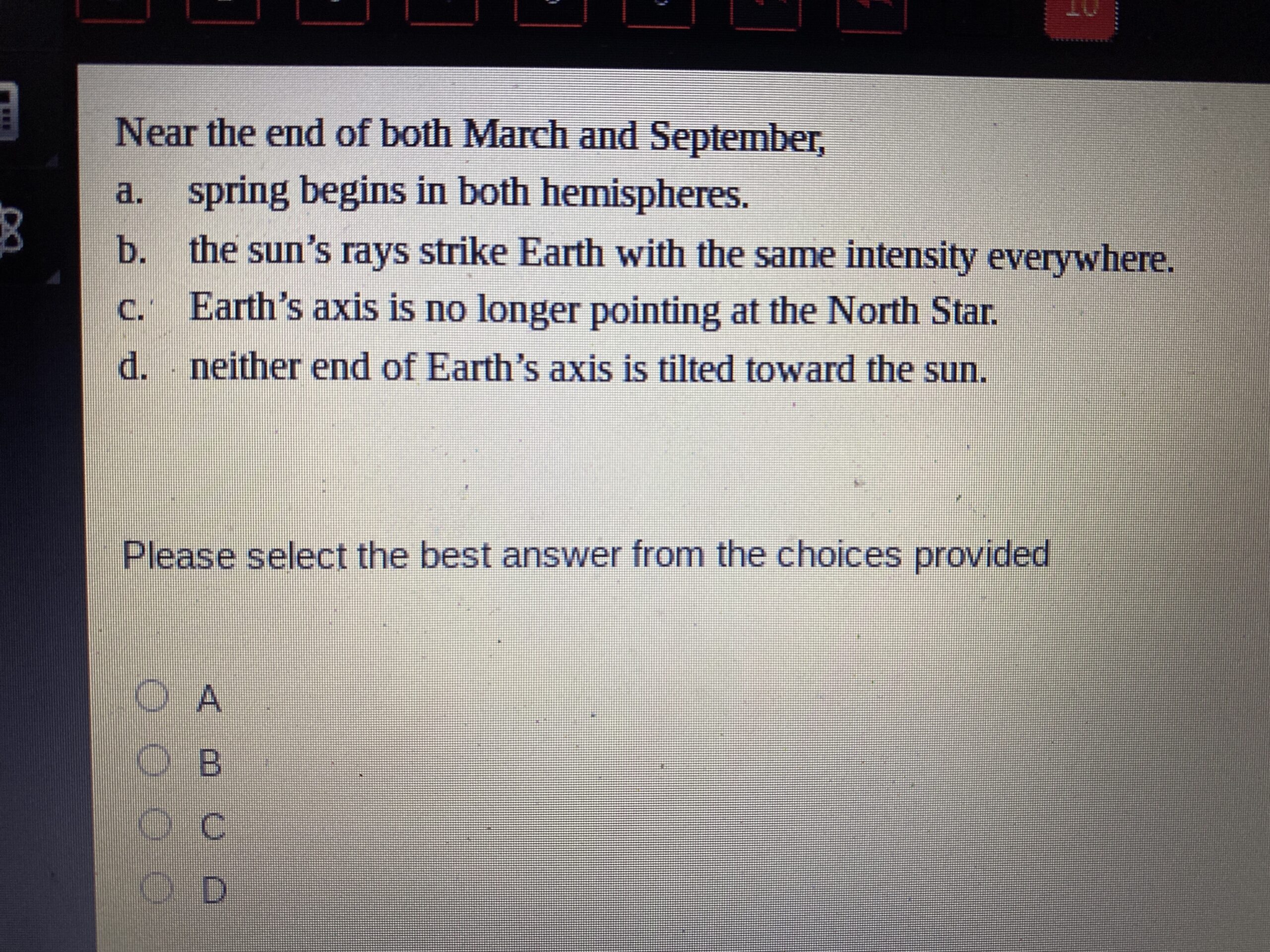
Near The End Of Both March And September A Spring Begins In Both Hemis
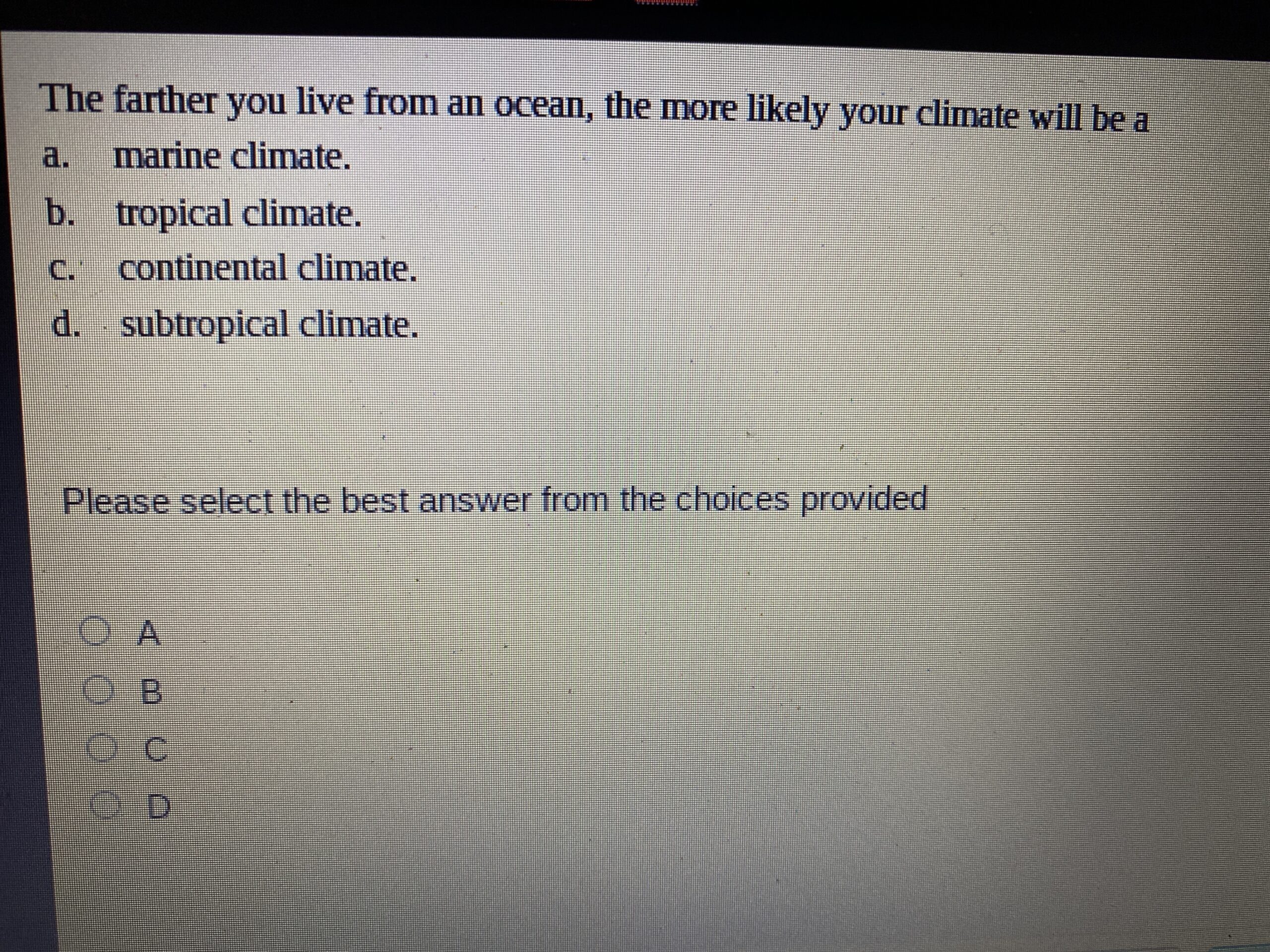
The Farther You Live From An Ocean The More Likely Your Climate Will Be
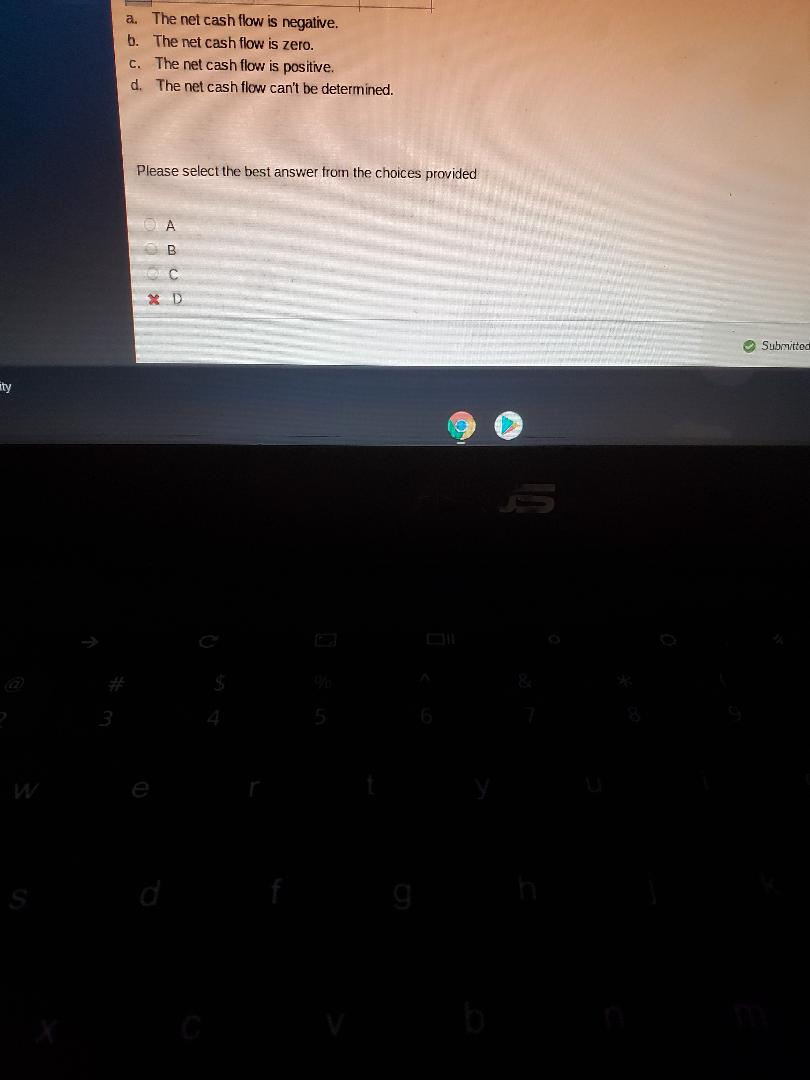
Solved Based On The Spreadsheet Below Which Of The Chegg
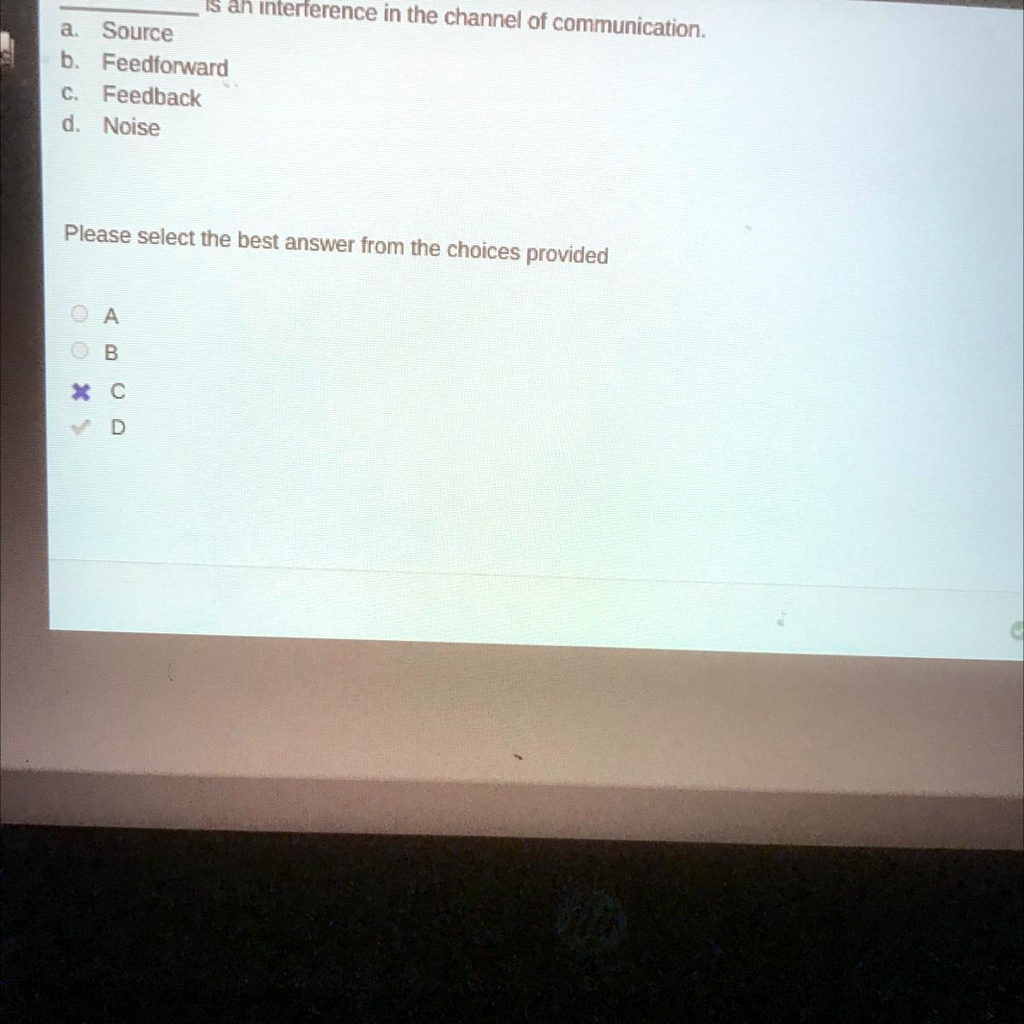
Is An Interference In The Channel Of Communication A Source B Feedforward C Feedback D Noise